Genetically engineered macrophages, solid tumors
- Categories:Industry News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2021-05-13 16:24
- Views:
Genetically engineered macrophages, solid tumors
(Summary description)On March 18, 2021, Carisma Therapeutics of the United States (hereinafter referred to as Carisma) announced the completion of the first patient administration of CAR-M therapy (CT-0508) targeting Her2, marking CAR-M transformation for the treatment of solid tumors Enter a new era.
In recent years, the engineering of CAR innate immune cells has received widespread attention. Among them, CAR-modified macrophages (CAR-Mac) are considered to be a cell type that is expected to overcome the limitations of CAR-T therapy and has a promising future in conquering solid tumors.
Macrophage mechanism of action
Macrophages activate lymphatic or other immune cells by engulfing cell debris and pathogens in body fluids and tissues and presenting antigens to make them respond to pathogens. In the tumor microenvironment, macrophages are the innate immune cells with the highest infiltration rate and can interact with almost all cellular components in TME, stimulate angiogenesis, increase tumor invasion, and mediate immunosuppression (1).
Tumor-associated macrophages (tumor-associated macrophage, TAM) are widely present in the microenvironment of solid tumors (tumor microenvironment, TME), and have important functions such as phagocytosis and killing of pathogens, processing and presentation of antigens. After activated, M1 type macrophages have a strong antigen-presenting ability and secrete reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are associated with a good prognosis of cancer (2).
Difficulties of engineered macrophage technology
(1) Macrophages are the first responders to viral infections in the human body and have a strong efflux effect on viruses, making it difficult for macrophages to be transfected by standard viral vectors used in gene therapy and cell therapy.
(2) The ability of primary macrophages to expand in vitro is weak in vitro.
Pre-clinical research data show promising prospects
Carisma's preclinical research results show that CAR-Mac exhibits antigen-specific phagocytosis and tumor killing effects in in vitro experiments. It is not only effective on target-positive tumor cells, but also has a certain killing effect on target-negative tumor cells. It is functionally similar to the original Tumor vaccine. In solid tumor xenograft mouse models, a single injection of CAR-Mac can significantly reduce tumor burden and prolong overall survival (fig 1). In humanized mouse model experiments, CAR-Mac can induce the production of pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment and enhance the activity of anti-tumor T cells. In the presence of immunosuppressive cells, CAR-Mac can still kill tumors. Further analysis of the cell viability characterization results showed that CAR-M can express pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, convert M2 type macrophages to M1 type, up-regulate the antigen presentation mechanism, recruit antigens and present them to T cells , While resisting the role of immunosuppressive cytokines (3).
Fig1. A: CAR-M treated mice demonstrated a marked reduction in tumor burden; B: CAR-Ms conferred a prolongation of overall survival.
References
1. Chen Y, Yu Z,Tan X, Jiang H, Xu Z, Fang Y, et al. CAR-macrophage: A newimmunotherapy candidate against solid tumors. Biomed Pharmacother.2021;139:111605.
2. Jayasingam SD, CitartanM, Thang TH, Mat Zin AA, Ang KC, Ch'ng ES. Evaluating the Polarization ofTumor-Associated Macrophages Into M1 and M2 Phenotypes in Human Cancer Tissue:Technicalities and Challenges in Routine Clinical Practice. Front Oncol.2019;9:1512.
3. Klichinsky M, Ruella M,Shestova O, Lu XM, Best A, Zeeman M, et al. Human chimeric antigen receptormacrophages for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38(8):947-53.
- Categories:Industry News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2021-05-13 16:24
- Views:
On March 18, 2021, Carisma Therapeutics of the United States (hereinafter referred to as Carisma) announced the completion of the first patient administration of CAR-M therapy (CT-0508) targeting Her2, marking CAR-M transformation for the treatment of solid tumors Enter a new era.
In recent years, the engineering of CAR innate immune cells has received widespread attention. Among them, CAR-modified macrophages (CAR-Mac) are considered to be a cell type that is expected to overcome the limitations of CAR-T therapy and has a promising future in conquering solid tumors.
Macrophage mechanism of action
Macrophages activate lymphatic or other immune cells by engulfing cell debris and pathogens in body fluids and tissues and presenting antigens to make them respond to pathogens. In the tumor microenvironment, macrophages are the innate immune cells with the highest infiltration rate and can interact with almost all cellular components in TME, stimulate angiogenesis, increase tumor invasion, and mediate immunosuppression (1).
Tumor-associated macrophages (tumor-associated macrophage, TAM) are widely present in the microenvironment of solid tumors (tumor microenvironment, TME), and have important functions such as phagocytosis and killing of pathogens, processing and presentation of antigens. After activated, M1 type macrophages have a strong antigen-presenting ability and secrete reactive oxygen species (ROS) and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are associated with a good prognosis of cancer (2).
Difficulties of engineered macrophage technology
(1) Macrophages are the first responders to viral infections in the human body and have a strong efflux effect on viruses, making it difficult for macrophages to be transfected by standard viral vectors used in gene therapy and cell therapy.
(2) The ability of primary macrophages to expand in vitro is weak in vitro.
Pre-clinical research data show promising prospects
Carisma's preclinical research results show that CAR-Mac exhibits antigen-specific phagocytosis and tumor killing effects in in vitro experiments. It is not only effective on target-positive tumor cells, but also has a certain killing effect on target-negative tumor cells. It is functionally similar to the original Tumor vaccine. In solid tumor xenograft mouse models, a single injection of CAR-Mac can significantly reduce tumor burden and prolong overall survival (fig 1). In humanized mouse model experiments, CAR-Mac can induce the production of pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment and enhance the activity of anti-tumor T cells. In the presence of immunosuppressive cells, CAR-Mac can still kill tumors. Further analysis of the cell viability characterization results showed that CAR-M can express pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, convert M2 type macrophages to M1 type, up-regulate the antigen presentation mechanism, recruit antigens and present them to T cells , While resisting the role of immunosuppressive cytokines (3).
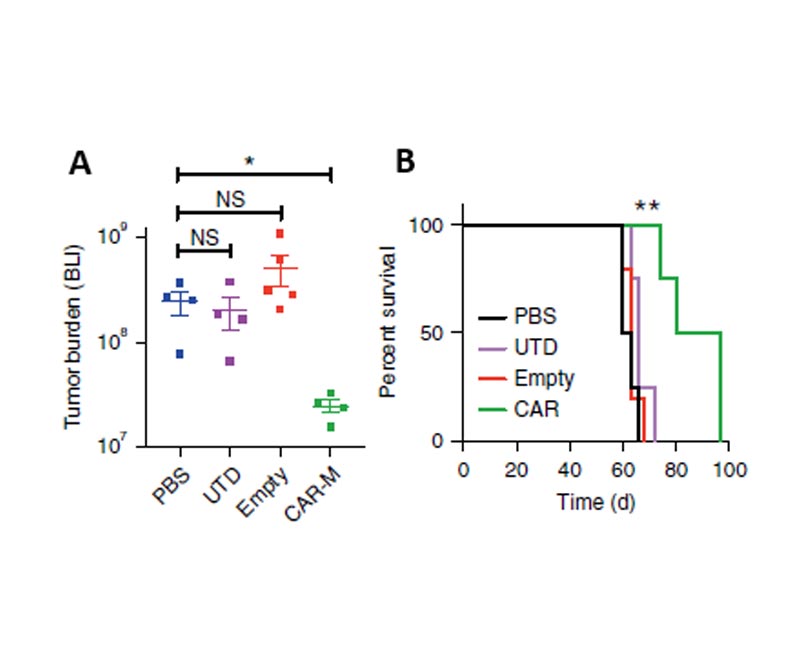
Fig1. A: CAR-M treated mice demonstrated a marked reduction in tumor burden; B: CAR-Ms conferred a prolongation of overall survival.
References
1. Chen Y, Yu Z,Tan X, Jiang H, Xu Z, Fang Y, et al. CAR-macrophage: A newimmunotherapy candidate against solid tumors. Biomed Pharmacother.2021;139:111605.
2. Jayasingam SD, CitartanM, Thang TH, Mat Zin AA, Ang KC, Ch'ng ES. Evaluating the Polarization ofTumor-Associated Macrophages Into M1 and M2 Phenotypes in Human Cancer Tissue:Technicalities and Challenges in Routine Clinical Practice. Front Oncol.2019;9:1512.
3. Klichinsky M, Ruella M,Shestova O, Lu XM, Best A, Zeeman M, et al. Human chimeric antigen receptormacrophages for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38(8):947-53.


Public Account

Official Website
Copyright© 2021 CellOrigin Technology (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd. 浙ICP备2021012934号 Powered by 300.cn

